Understanding what is the difference between vestibule and anteroom is crucial for architects, builders, and anyone involved in space design. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct architectural concepts with unique purposes and applications. This comprehensive guide explores their definitions, historical contexts, modern uses, and practical construction considerations to help you make informed decisions for your next project. Visit NatureGuests for more architectural insights.
Understanding Basic Definitions and Terminology
When exploring what is the difference between vestibule and anteroom, we must first establish clear definitions. A vestibule is primarily an architectural transitional space that serves as a buffer between the exterior and interior of a building. This small room or hall typically functions as an airlock entry, helping to reduce heat loss, provide storage for outdoor clothing, and create a welcoming entrance experience.
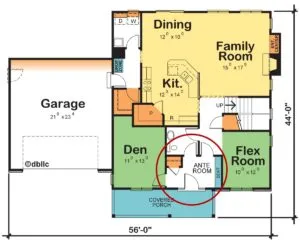
An anteroom, on the other hand, derives its name from the Latin "ante" meaning "before" and serves as a waiting room or preparatory space before entering a more significant area. While anterooms can function similarly to vestibules in some contexts, they often have specific operational purposes beyond simple transitional space management.
The key distinction lies in their primary functions: vestibules focus on environmental control and transition, while anterooms emphasize preparation and waiting. Both serve important roles in modern architecture, and understanding their unique characteristics helps architects and builders make informed design decisions. For outdoor enthusiasts planning shelter solutions, concepts similar to vestibules can be found in high-altitude tent designs where transitional spaces provide crucial weather protection.
Modern building codes and energy efficiency standards have elevated the importance of both vestibules and anterooms. These spaces contribute significantly to HVAC efficiency, security protocols, and user experience design. Professional architects often specify detailed requirements for these transitional areas based on building size, climate conditions, and intended use patterns.
Historical Context and Architectural Evolution
The historical development of vestibules and anterooms reveals fascinating insights into what is the difference between vestibule and anteroom in terms of cultural and practical evolution. Ancient Roman architecture featured vestibula as semi-enclosed spaces between the street and the interior fauces, serving both practical and ceremonial purposes. These early vestibules demonstrated the Roman understanding of transitional spaces as essential architectural elements.
Medieval and Renaissance palaces showcased elaborate anterooms where visitors would wait before being received in throne rooms or state chambers. These anterooms often featured ornate decorations and served as displays of wealth and power. The Genoese palazzo tradition particularly emphasized grand vestibules that could accommodate "a race of giants," highlighting the ceremonial importance of these transitional spaces.
Church architecture from the 5th century onward utilized both concepts extensively. Vestibules in churches served as narthexes, providing space for catechumens and penitents, while anterooms adjacent to sanctuaries offered preparation areas for clergy. This religious application demonstrates how architectural terminology evolved to serve specific functional requirements. Similar principles can be observed in traditional shelter designs like Viking tent structures that incorporated transitional spaces for practical purposes.
The Industrial Revolution brought new considerations to vestibule and anteroom design, particularly regarding air quality, temperature control, and mass building construction. Victorian architecture embraced elaborate entrance halls and reception rooms that blended vestibule and anteroom functions, creating sophisticated transitional sequences that managed both environmental and social interactions effectively.
Key Differences in Design and Function
Understanding what is the difference between vestibule and anteroom requires examining their distinct design philosophies and functional priorities. Vestibules prioritize environmental control, featuring double-door systems, weather seals, and climate transition management. They typically include features like boot storage, coat hooks, and drainage systems to handle outdoor elements.
Anterooms focus on human interaction and preparation activities. They often include seating areas, reception desks, information displays, and storage for items needed in adjacent spaces. The sizing and layout of anterooms reflect their role as gathering and preparation spaces rather than simple transitional corridors.
Size requirements differ significantly between these spaces. Vestibules can be quite compact, requiring only enough space for door operations and basic storage. Anterooms typically need larger floor areas to accommodate their expanded functional requirements. Commercial building codes specify minimum dimensions based on occupancy loads and accessibility requirements.
Transform Your Entrance Today!
Create the perfect vestibule or anteroom with professional-grade solutions
🔧 ZipWall Hall Kit - $185.91Ventilation and air quality management represent another crucial distinction. Vestibules require sophisticated HVAC integration to manage temperature differentials and prevent energy loss. Anterooms may have simpler ventilation needs but often require better acoustic treatment to support conversation and waiting activities. Modern tent designs incorporating similar principles can be found in DCF tent technologies that balance protection with ventilation needs.
Modern Applications and Use Cases
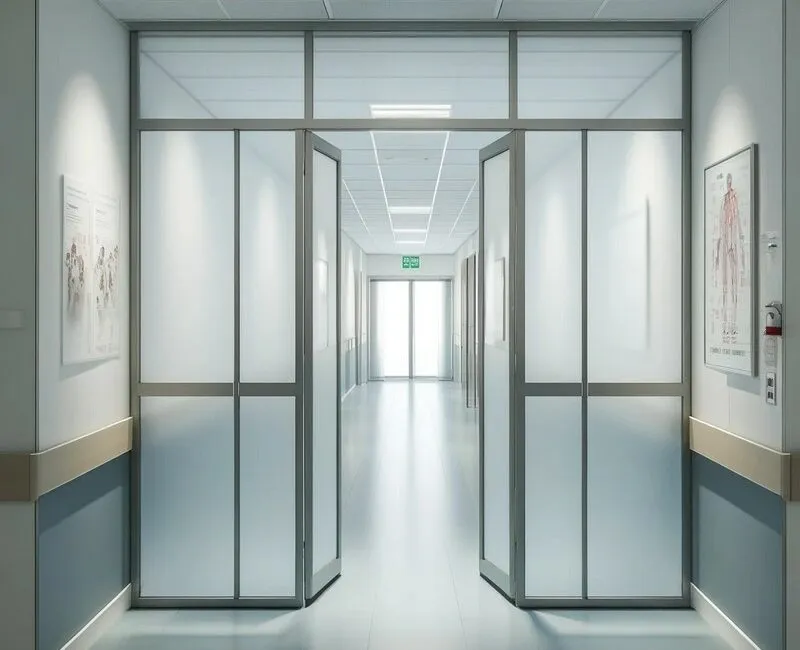

Contemporary architecture showcases diverse applications that highlight what is the difference between vestibule and anteroom in practical terms. Healthcare facilities utilize both concepts extensively: vestibules at main entrances manage contamination control and temperature regulation, while anterooms adjacent to operating theaters provide sterile preparation areas for medical staff.
Educational institutions demonstrate varied applications based on specific needs. School main entrances feature vestibules for security screening and weather protection, while specialized anterooms serve laboratories, performance spaces, and administrative areas. The design requirements differ significantly based on user patterns and safety protocols.
Commercial office buildings increasingly recognize the value of well-designed entrance sequences. Vestibules provide professional first impressions while managing energy efficiency requirements. Executive floors often feature anterooms for reception and informal meeting purposes. High-tech industries may require specialized anterooms for security clearance and equipment transition.
💡 Pro Tip for Space Planning
When planning transitional spaces, consider traffic flow patterns and peak usage times. Vestibules need efficient circulation paths, while anterooms benefit from flexible seating arrangements and clear sight lines to adjacent areas.
Residential applications reflect lifestyle and climate considerations. Luxury homes often feature formal vestibules with architectural details, while practical mudrooms serve vestibule functions for family entrances. Anterooms appear in home offices, master bedroom suites, and entertainment areas where transition and preparation activities occur. Understanding these distinctions helps avoid issues similar to those found in dome tent design limitations where improper space planning creates functional problems.
Construction Materials and Design Solutions

Material selection for vestibules and anterooms reflects their different functional priorities, further illustrating what is the difference between vestibule and anteroom in construction terms. Vestibule flooring must handle moisture, snow, and heavy traffic, requiring materials like ceramic tile, polished concrete, or commercial-grade vinyl with proper drainage systems.
Anteroom materials emphasize comfort and aesthetics while maintaining durability. Carpet, hardwood, or luxury vinyl planking create welcoming environments suitable for extended occupancy. Wall treatments may include acoustic panels, decorative finishes, or specialized surfaces depending on the anteroom's specific function.
Professional Construction Solutions
Upgrade your space with high-quality materials and furniture
🎨 Art3d Wall Panels - $99.67 🪑 SONGMICS Hall Tree - $39.99Lighting design varies significantly between these spaces. Vestibules require bright, even illumination for safety and security purposes, often incorporating motion sensors and emergency lighting systems. Anterooms benefit from layered lighting schemes that create comfortable ambiance while supporting specific activities like reading or conversation.
Climate control systems must address different challenges in each space type. Vestibules need robust systems capable of handling rapid temperature changes and potential moisture loads. Anterooms require stable, comfortable environments similar to primary occupied spaces, with particular attention to air quality and circulation patterns.
Technology integration represents an increasingly important construction consideration. Vestibules may incorporate security systems, access controls, and communication devices. Anterooms often feature information displays, telecommunications infrastructure, and specialty equipment based on their specific applications. Smart building systems can optimize both space types for energy efficiency and user experience.
Practical Planning and Implementation
Successful implementation requires understanding how what is the difference between vestibule and anteroom translates into practical design decisions. Budget allocation differs significantly between these space types, with vestibules requiring higher investment in mechanical systems and weather-resistant materials, while anterooms emphasize furnishings and finishes.
Code compliance presents unique challenges for each space type. Vestibules must meet specific requirements for egress, accessibility, and energy efficiency. Many jurisdictions require vestibules for commercial buildings over certain square footage thresholds. Anterooms face regulations related to their specific functions, such as fire safety requirements for assembly areas or contamination controls for healthcare applications.
Complete Your Space Setup
Essential equipment for temporary and permanent installations
🏠 Bush Furniture Hall Tree - $172.99 🚪 Room Divider System - $31.99Maintenance considerations affect long-term operational costs and user satisfaction. Vestibules typically require more frequent cleaning and maintenance due to weather exposure and heavy traffic. Drainage systems, door mechanisms, and climate control equipment need regular attention. Anterooms generally have lower maintenance requirements but may need periodic furniture updates and technology refreshes.
User experience design plays a crucial role in both space types. Vestibules should facilitate smooth traffic flow while providing clear wayfinding and comfortable transition experiences. Anterooms must balance functional requirements with user comfort, incorporating appropriate furniture, storage, and amenities. Regular user feedback helps optimize both space types for maximum effectiveness.
Future adaptability represents an important planning consideration. Building needs evolve over time, and transitional spaces must accommodate changing requirements. Flexible design approaches allow vestibules and anterooms to adapt to new technologies, security requirements, or functional needs without major reconstruction. For comprehensive planning resources and related architectural insights, visit our detailed guide on vestibule and anteroom differences.
Conclusion
Understanding what is the difference between vestibule and anteroom empowers architects, builders, and property owners to make informed decisions about transitional space design. These architectural elements serve distinct but complementary functions in modern building design, each contributing to user experience, energy efficiency, and operational effectiveness.
Vestibules excel at environmental control and building protection, serving as crucial barriers between interior and exterior conditions. Their design priorities focus on durability, weather resistance, and efficient traffic management. Anterooms provide essential preparation and waiting functions, emphasizing user comfort, flexibility, and specific operational requirements.
Successful implementation of either space type requires careful consideration of function, materials, systems integration, and long-term maintenance needs. By recognizing the unique characteristics and requirements of vestibules versus anterooms, design professionals can create more effective, efficient, and user-friendly built environments.
The investment in well-designed transitional spaces pays dividends through improved energy efficiency, enhanced user experience, and better building performance. Whether planning a simple residential entrance or a complex commercial facility, understanding these fundamental differences ensures optimal results for any architectural project.
For more architectural insights and outdoor living solutions, explore our comprehensive guides at NatureGuests.com